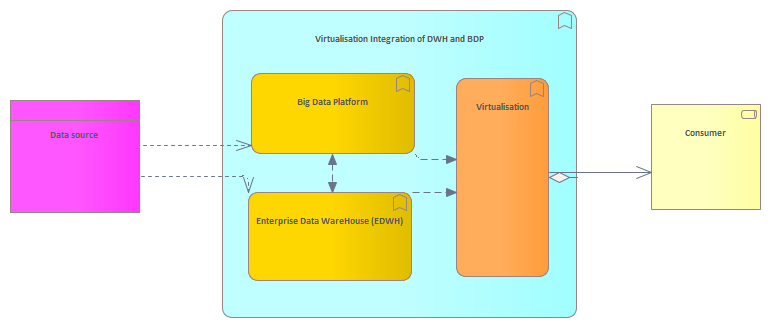
This integration pattern has a close relation with the parallel integration, however there is an extra layer introduced for the virtualisation and standardisation of data extraction to consumers of the data.
Characteristics
- Virtualisation layer encapsulate the internal confuguration of the two platforms
- The virtualisation layer requires a standardized data or objectmodel for the extraction by the consumers
- The virtualisation can become a bottleneck in a number of qualities like performance, integratability e.g.
-